
 |
Charlotte Stonestreet
Managing Editor |
| Home> | Guides | >MAD Guide | >High Efficiency Electric Motor Bearings Reduce Friction by 35% and Noise by 50% |
ARTICLE
High Efficiency Electric Motor Bearings Reduce Friction by 35% and Noise by 50%
23 January 2015
For designers of electric motors, as well as machine builders and appliance manufacturers, motor efficiency, noise and vibration levels are important design and quality criteria. Strict controls are now often placed on the motor regarding noise, environmental protection and occupational safety.
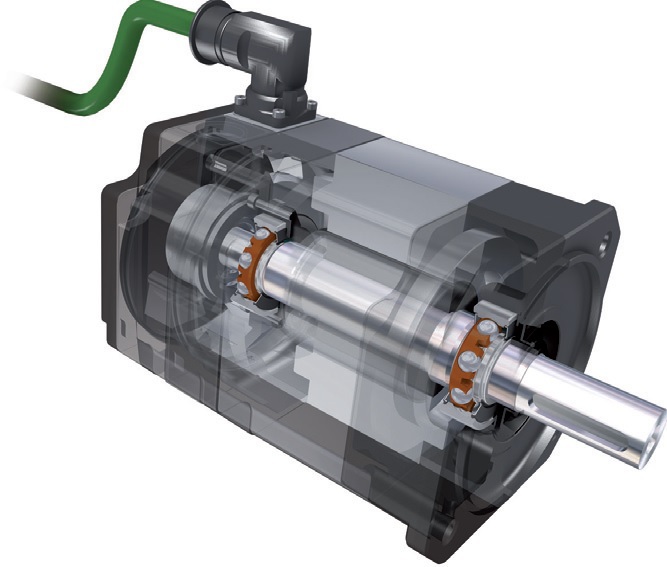
Following intensive analysis of the causes of noise, Schaeffler has improved the internal design of its deep groove ball bearings for small electric motors. These improvements include improved raceway surfaces, improved ball quality, tighter manufacturing tolerances, new riveted steel cages and a large selection of special greases.
The ‘Generation C’ range of deep groove ball bearings from Schaeffler not only offer 35% less friction than their predecessors, but also cut noise levels by 50%. This means a more efficient motor, resulting in reduced energy consumption. The design improvements mean that the bearings can achieve higher running speeds, whilst simultaneously increasing the operating life of the bearing.
Generation C bearings are ideal for applications in which low noise and smooth running are critical. Reduced friction levels and improved energy efficiency from the bearings means a reduction in running costs for plant operators and a more efficient machine with extended maintenance intervals.
In order to reduce friction by 35%, Schaeffler has optimised the raceway geometry, which means there is less chance of misalignment between the inner and outer ring.
As well as offering less friction, the bearings also generate less heat, making them suitable for higher running speeds.
The bearings have improved sealing due to the optimised position of the lip seals, HRS.
Made from nitrile butadiene rubber, the HRS seals now have modified double lip geometry and have been adjusted to match the recess on the bearing inner ring. Axial contact between the inner ring and the seal means more effective protection against contamination or loss of grease and less frictional torque. This results in longer grease life, increasing the life and reliability of the bearing and provides improved bearing performance at higher speeds.
In addition to the HRS seal, the bearing shield has been modified. The recesses on the bearing rings and the shield geometry are functionally adjusted to each other in such a way that the sealing efficiency is improved and grease life increased. This design creates an axial and radial labyrinth with the shield.
The improved guidance of the rolling elements also contributes to higher performance of the bearing. The new twopiece riveted steel cage, which replaces the previous steel lug cage, offers higher rigidity and so is suitable for higher running speeds. The riveted steel cage also reduces noise levels and means the bearing is less sensitive to shock loads. The dimensional and geometrical tolerances correspond to tolerance class P6 to DIN 620-2 (ISO 492). Bearings of higher accuracy (P5) are available upon agreement.
The boundary dimensions of the new bearings correspond to the previous bearing types, enabling easy replacement. Generation C bearings can operate in temperatures from - 30°C to +120°C.
The bearings are available with outer diameters from 26mm up to 90mm. A more stable riveted steel metal cage is now used as standard for Generation C bearings, or optional polyamide cages. Sealing options include one or two gap seals; one or two lip seals; or low friction, non-contact labyrinth seals.
MORE FROM THIS COMPANY
- RAIL TEST RIG FOR AXLEBOX BEARINGS
- Innovative components for LWRs and cobots
- Schaeffler to sponsor female NMITE student
- Condition monitoring helps prevent unplanned downtime
- Bearing coating for current passage protection
- Online condition monitoring prevents unplanned downtime
- Innovative solution package for robotics industry
- Schaeffler acquires Elmotec Statomat
- Counterfeit bearings put end users & distributors at risk
- Lowering beverage industry production costs
RELATED ARTICLES
- Robotics & Automation 2013
- Automation on the upswing
- Amendment to Commission Regulation (EC) No 640/2009
- Confidence returning to UK manufacturing technologies
- A national success story
- Automation: plan to succeed
- EPTDA expands in the Middle East & Africa
- Innovating for the recovery, innovating for the future
- A system-oriented approach to assessing energy efficiency
- tGARD IN ACTION
OTHER ARTICLES IN THIS SECTION


















